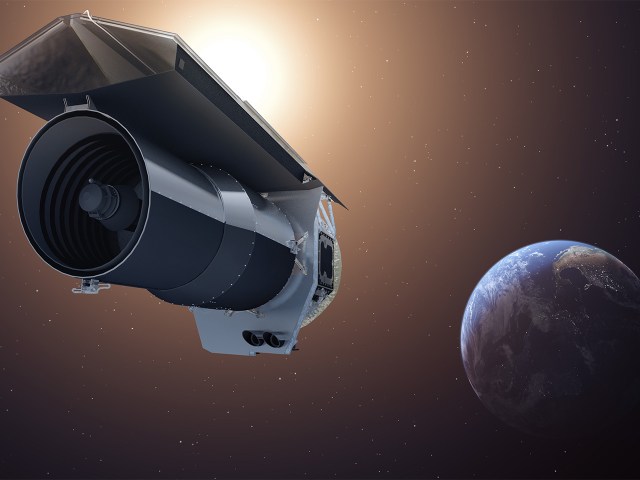
As Spitzer enters the Beyond phase of its mission, the spacecraft’s unique orbit and age bring about new engineering challenges. Spitzer trails behind Earth in its journey around the sun, but due to its slower travel speed, the distance between Spitzer and Earth has gradually widened over time. This means that in order to maintain communication with Earth, Spitzer’s antenna must be pointed at higher angles towards the sun as it gets farther away. Consequently, parts of the spacecraft will be exposed to increasing levels of heat.
Another challenge presented by Spitzer’s orbit is that the spacecraft’s solar panels, which provide power to the spacecraft, will receive less sunlight as they point away from the sun. This will put additional stress on the batteries of the spacecraft as they try to maintain the necessary power levels for operation. In order to enable this riskier mode of operations in the Beyond phase, the mission team will need to override certain autonomous safety systems that would normally take action to protect the spacecraft from potential hazards. This will require close monitoring and coordination to ensure the continued success of the Spitzer mission.